When a material is stretched in one direction, it will usually shrink in the other perpendicular directions.
The Poisson’s ratio, ![]() , is the ratio of transverse strain,
, is the ratio of transverse strain, ![]() to axial strain
to axial strain ![]() , where an axial force has been applied.
, where an axial force has been applied.
(1) ![]()
The strain of a material is defined as:
(2) ![]()
Where ![]() = change in length,
= change in length, ![]() = original length.
= original length.
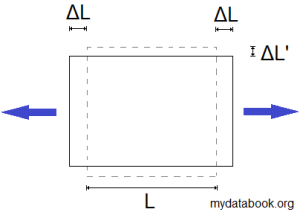
Poisson’s ratio will typically be between 0 to 0.5 for most common materials.
Approximation for Very Small Strains
For very small changes in length, an approximation for Poisson’s ratio is:
(3) ![]()
Typical Poisson’s Ratios for Common Materials
| Material | Poisson’s Ratio |
| Aluminium | 0.32 – 0.35 |
| Aluminium Alloys | 0.32 – 0.35 |
| Boron Carbide (B4C) | 0.15 – 0.18 |
| Brass | 0.34 |
| Brick | 0.19 |
| Bronze | 0.34 |
| Carbon (Diamond) | 0.20 |
| Concrete | 0.2 |
| Copper | 0.33 – 0.35 |
| Cork | 0 |
| Glass | 0.2 – 0.22 |
| Gold | 0.4 |
| Iron | 0.22 – 0.3 |
| Magnesium | 0.29 |
| Nickel | 0.31 |
| Nylon | 0.39 – 0.42 |
| Platinum | 0.38 – 0.4 |
| Rubber | 0.49 |
| Silver | 0.37 |
| Solder (Tin-Lead) | 0.4 |
| Steel | 0.27 – 0.3 |
| Stone (Granite) | 0.2 – 0.3 |
| Stone (Limestone) | 0.2 – 0.3 |
| Stone (Marble) | 0.2 – 0.3 |
| Tin | 0.32 – 0.36 |
| Titanium | 0.32 |
| Tungsten | 0.28 |
| Zinc | 0.25 |