Speed of Sound in a Liquid (Static Fluid Wave Speed)
In a fluid at rest, the wave speed of a fluid is equivalent to the speed of sound in the same medium, whether liquid or gas.
The speed of sound is calculated from the Newton-Laplace equation:
(1) 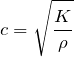
Where c = speed of sound, K = bulk modulus or stiffness coefficient, ρ = density.
Where a pressure wave passes through a liquid contained within an elastic vessel, the liquid’s density and therefore the wave speed will change as the pressure wave passes. This is commonly experienced as water hammer.